Today we (Chamseddine-Connes-van Suijlekom) posted a preprint on grand unification in the spectral Pati–Salam model which I summarize here.
The paper builds on two recent discoveries in the noncommutative geometry approach to particle physics: we showed how to obtain inner fluctuations of the metric without having to assume the order one condition on the Dirac operator. Moreover the original argument by classification of finite geometries \(F\) that can provide the fine structure of Euclidean space-time as a product \(M\times F\) (where \(M\) is a usual 4-dimensional Riemannian space) has now been replaced by a much stronger uniqueness statement. This new result shows that the algebra
\(
M_{2}(\mathbb{H})\oplus M_{4}(\mathbb{C})
\)
where \(\mathbb{H}\) are the quaternions, appears uniquely when writing the higher analogue of the Heisenberg commutation relations. This analogue is written in terms of the basic ingredients of noncommutative geometry where one takes a spectral point of view, encoding geometry in terms of operators on a Hilbert space \(\mathcal{H}\). In this way, the inverse line element is an unbounded self-adjoint operator \(D\). The operator \(D\) is the product of the usual Dirac operator on \(M\) and a `finite Dirac operator’ on \(F\), which is simply a hermitian matrix \(D_{F}\). The usual Dirac operator involves gamma matrices which allow one to combine the momenta into a single operator. The higher analogue of the Heisenberg relations puts the spatial variables on similar footing by combining them into a single operator \(Y\) using another set of gamma matrices and it is in this process that the above algebra appears canonically and uniquely in dimension 4.
This leads without arbitrariness to the Pati–Salam gauge group \(SU(2)_{R}\times SU(2)_{L}\times SU(4)\), together with the corresponding gauge fields and a scalar sector, all derived as inner perturbations of \(D\). Note that the scalar sector can not be chosen freely, in contrast to early work on Pati–Salam unification. In fact, there are only a few possibilities for the precise scalar content, depending on the assumptions made on the finite Dirac operator.
From the spectral action principle, the dynamics and interactions are described by the spectral action,
\(
\mathrm{tr}(f(D/\Lambda))
\)
where \(\Lambda\) is a cutoff scale and \(f\) an even and positive function. In the present case, it can be expanded using heat kernel methods,
\(\mathrm{tr}(f(D/\Lambda))\sim F_{4}\Lambda^{4}a_{0}+F_{2}\Lambda^{2}%
a_{2}+F_{0}a_{4}+\cdots
\)
where \(F_{4},F_{2},F_{0}\) are coefficients related to the function \(f\) and \(a_{k}\) are Seeley deWitt coefficients, expressed in terms of the curvature of \(M\) and (derivatives of) the gauge and scalar fields. This action is interpreted as an effective field theory for energies lower than \(\Lambda\).
One important feature of the spectral action is that it gives the usual Pati–Salam action with unification of the gauge couplings. Indeed, the scale-invariant term \(F_{0}a_{4}\) in the spectral action for the spectral Pati–Salam model contains the terms
\(
\frac{F_{0}}{2\pi^{2}}\int\left( g_{L}^{2}\left( W_{\mu\nu L}^{\alpha
}\right) ^{2}+g_{R}^{2}\left( W_{\mu\nu R}^{\alpha}\right) ^{2}%
+g^{2}\left( V_{\mu\nu}^{m}\right) ^{2}\right) .
\)
Normalizing this to give the Yang–Mills Lagrangian demands
\(
\frac{F_{0}}{2\pi^{2}}g_{L}^{2}=\frac{F_{0}}{2\pi^{2}}g_{R}^{2}=\frac{F_{0}%
}{2\pi^{2}}g^{2}=\frac{1}{4},
\)
which requires gauge coupling unification. This is very similar to the case of the spectral Standard Model where there is unification of gauge couplings. Since it is well known that the SM gauge couplings do not meet exactly, it is crucial to investigate the running of the Pati–Salam gauge couplings beyond the Standard Model and to find a scale \(\Lambda\) where there is grand
unification:
\(
g_{R}(\Lambda)=g_{L}(\Lambda)=g(\Lambda).
\)
This would then be the scale at which the spectral action is valid as an effective theory. There is a hierarchy of three energy scales: SM, an intermediate mass scale \(m_{R}\) where symmetry breaking occurs and which is related to the neutrino Majorana masses (\(10^{11}-10^{13}\)GeV), and the GUT scale \(\Lambda\).
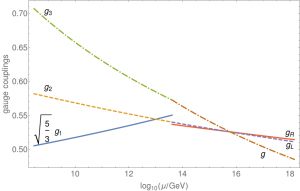
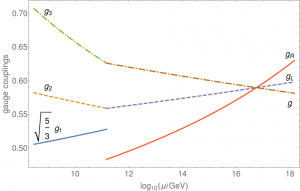
In the paper, we analyze the running of the gauge couplings according to the usual (one-loop) RG equation. As mentioned before, depending on the assumptions on \(D_{F}\), one may vary to a limited extent the scalar particle content, consisting of either composite or fundamental scalar fields. We will not limit ourselves to a specific model but consider all cases separately. This leads to the following three figures:
In other words, we establish grand unification for all of the scenarios with unification scale of the order of \(10^{16}\) GeV, thus confirming validity of the spectral action at the corresponding scale, independent of the specific form of \(D_{F}\).